Melting Glaciers in Indian Himalayas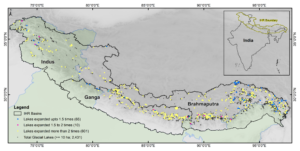
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has released a new study highlighting a concerning trend: glacial melt across the Indian Himalayas is leading to a significant expansion of glacial lakes. While these lakes are vital freshwater sources for the region’s rivers, their growth poses a serious threat – an increased risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) with potentially devastating consequences for downstream communities.
Melting Glaciers, Expanding Lakes: A Cause for Concern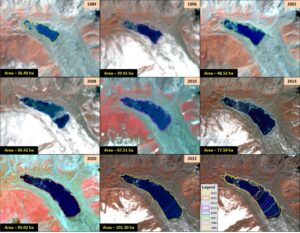
The Himalayas, often referred to as the “Third Pole” due to their vast reserves of freshwater ice, are highly vulnerable to climate change. Research worldwide confirms a consistent pattern – glaciers around the globe have been retreating and thinning at unprecedented rates since the Industrial Revolution. This retreat is a key factor in the formation and expansion of glacial lakes in the Himalayan region.
ISRO’s study utilized satellite data spanning nearly four decades. The analysis revealed significant changes in glacial lakes across the Indian Himalayas. Over 2,400 glacial lakes were identified in the 2016-17 timeframe, with a worrying trend: 676 of these lakes have shown considerable expansion since 1984. This includes a troubling 130 lakes located within India, spread across various river basins.
The Threat of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs)
While glacial lakes act as crucial freshwater sources, their growth also presents a significant risk – GLOFs. These catastrophic events occur when glacial lakes release large volumes of meltwater due to the sudden failure of natural dams, often composed of moraine or ice. These dam failures can be triggered by various factors, including avalanches of ice or rock, extreme weather events, and other environmental changes.
The consequences of GLOFs can be devastating. The sudden release of massive amounts of water can cause flash floods downstream, inundating villages, destroying infrastructure, and displacing communities. The 2013 Kedarnath disaster in India serves as a stark reminder of the destructive potential of GLOFs. In that event, a series of cloudbursts triggered a glacial lake outburst, leading to widespread flash floods that caused immense loss of life and property.
ISRO’s Role in Monitoring and Risk Assessment
The rugged and remote terrain of the Himalayas makes it challenging to monitor and study glacial lakes on the ground. However, satellite remote sensing technology offers a valuable solution. Its wide coverage and ability to revisit the same areas frequently makes it an excellent tool for creating inventories and monitoring changes in glacial lakes.
By analyzing long-term satellite data archives, scientists can gain valuable insights into changes occurring in glaciated environments. The ISRO study employed data spanning 3-4 decades to assess long-term trends in glacial lake area. This information is crucial for understanding glacier retreat rates, evaluating GLOF risks, and gaining a deeper understanding of climate change’s impact on the Himalayas.
Looking Ahead: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
The findings of the ISRO study underscore the urgent need for effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. Combating climate change is a key long-term solution, requiring global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
On a regional level, proactive measures are necessary to minimize GLOF risks. Early warning systems can be crucial in providing downstream communities with vital lead time to prepare for potential floods. Additionally, structural measures, such as reinforcing natural dams or constructing artificial dams, can be explored in high-risk areas.
Investing in research and development is also essential. Further studies are needed to improve our understanding of factors triggering GLOFs and develop more accurate prediction models. This knowledge will be vital for implementing effective risk reduction strategies.
The Himalayas are a vital source of freshwater for millions in India and beyond. Protecting these glaciers and mitigating the risks associated with glacial melt is not just an environmental imperative, but also a matter of ensuring the safety and well-being of downstream communities. By taking proactive steps based on scientific data, such as the one provided by ISRO, we can work towards a more sustainable future for the Himalayan region.
Melting Glaciers and Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) in the Indian Himalayas
1. What’s causing glaciers to melt in the Indian Himalayas?
The primary culprit is climate change. Rising global temperatures are accelerating the melting of glaciers across the Himalayas, including those in India.
2. Why are expanding glacial lakes a concern?
While these lakes are important freshwater sources, their rapid growth increases the risk of GLOFs. These sudden floods occur when the natural dams containing these lakes fail, releasing massive amounts of water downstream.
3. How dangerous are GLOFs?
GLOFs can be devastating. They can trigger flash floods that cause widespread damage to infrastructure, displace communities, and even lead to loss of life, as seen in the 2013 Kedarnath disaster.
4. How is ISRO helping monitor glacial lakes?
ISRO utilizes satellite data to track changes in glacial lakes. This data allows scientists to assess expansion trends, understand glacier retreat rates, and identify areas potentially at high risk of GLOFs.
5. What can be done to reduce GLOF risks?
Combating climate change is crucial in the long run. On a regional level, early warning systems, structural reinforcements for natural dams, and improved research on GLOF triggers are vital for mitigation and adaptation.





